Eating Disorders in the Asian American Community: A Call for Cultural Consciousness
Written by MEDA Undergraduate Intern, Lauren Kim
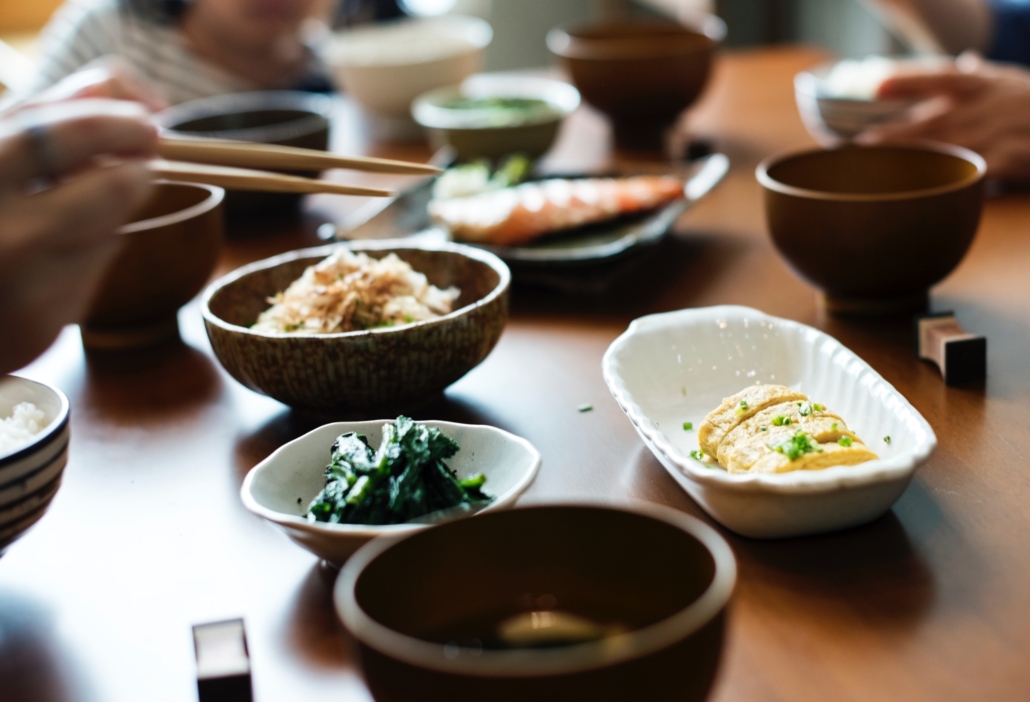
 If you’re Asian American, you know that there is nothing good about hunger. Many of our parents, whether they came to the country as immigrants or refugees, know real hunger. They make sure that we never leave the house without full bellies and greet us when we return with heaps of warm homemade food. Food is our love language – the one thing that transcends the language barriers, the cultural differences, the generation gaps, and all the other things that keep us from saying “I love you” out loud.
If you’re Asian American, you know that there is nothing good about hunger. Many of our parents, whether they came to the country as immigrants or refugees, know real hunger. They make sure that we never leave the house without full bellies and greet us when we return with heaps of warm homemade food. Food is our love language – the one thing that transcends the language barriers, the cultural differences, the generation gaps, and all the other things that keep us from saying “I love you” out loud.
But by twisted logic, food is also the enemy. If you’re Asian American, you also know that being fat in an Asian family is tantamount to falling short of making the honor roll. It is understood as an indication of personal weakness – a lack of discipline, laziness, failure. When you’re “fat” by Asian standards, it can be hard not to feel like a burden to your family because you’re told, either implicitly or explicitly, that the shame is not only carried by you, but by your family as well. And so, the burden of shame begins to feel even heavier.
What makes things exponentially more complicated is this idea of familial duty. Because so many Asian Americans are commonly raised on the rhetoric of hard work and sacrifice, we are ingrained with a deep desire to express our gratitude to our parents by fulfilling their hopes and dreams for us. For some, that might mean becoming a doctor or a lawyer. But for others, it could mean losing weight to get closer to the ideal Asian body – small, pale, and willowy thin.
One thing that sets Asian culture apart from others is the level of brutal honesty with which people speak. Time and time again, I’ve noticed that there is a general willingness to make comments, especially on other people’s appearances, which can be so abrasive that they sometimes err on the side of cruelty. When you are taught that being thin is a virtue, and that being heavy and being happy cannot be feasibly reconciled in one body, “fat” becomes the worst thing you can be called. So whether we want to or not, Asian Americans cannot help but internalize our culture’s guidelines on what a desirable body looks like, and by default, what its converse looks like.
Growing up, I resented the unreasonable expectations placed on me by my family and my culture and I looked to every family gathering with anxiety and dread. Being around extended family always meant one thing: that I’d have to bear hours of being force-fed excessive amounts of food by the same people who would tell me to my face that I had gained weight since the last time they saw me. And through it all, I would force a tight-lipped smile and try to maintain my composure. If I was ever so bold as to politely refuse the food that was offered, I’d be urged by my mother to “just be polite” and eat. And if I did accept the food and finished it, more would immediately be piled onto my plate, pressuring me to eat way past the point of fullness.
As my fellow Asian Americans know all too well, there is no winning when you grow up in this contradictory culture. The only thing that never seems to change is our culture’s steadfast commitment to a singular definition of beauty. In a world that has begun to promote loving yourself and finding beauty in your flaws, Asian culture has not managed to keep up. There’s an overbearing pressure to be perfect naturally, or to constantly be improving yourself if you’re not. This mentality helps to make sense of why plastic surgery is so prevalent and even normalized in Asian countries. Why love your flaws, when you can remove them, right?
It’s easy to see how these dangerous messages can encourage body dissatisfaction in the Asian American community and eventually manifest as an eating disorder. According to a statistic cited on the National Eating Disorders Association’s website, Asian, Black, Hispanic, and Caucasian youth have all reported attempting to lose weight at similar rates [1].
But there’s no way that you would know that, judging by what is commonly portrayed in the media. Eating disorders continue to be an issue that is typically attributed to white, straight, cis-gendered, able-bodied women of high-income backgrounds. Though we are slowly making progress in challenging this narrow-minded view of what someone with an eating disorder looks like, there is far more work to do. The lack of Asian Americans represented in the national discussion on eating disorders seems to indicate that many are still suffering in silence. According to Dr. Szu-Hui Lee, a clinical psychologist and director of training at the McLean Hospital at Harvard Medical School, Asian Americans tend to under-report mental health issues. She explains: “There’s a big stigma with seeing a psychologist. [Asian American] parents are more likely to send their kids to an academic counselor than a psychologist.” [2]
In a culture where optics matter so much, it is not hard to see why individuals with eating disorders struggle to speak up and ask for help. The stigma attached to mental illness is so severe in our culture that our parents are likely to respond to our pleas for help with fear, denial, blame, and anger.
As someone who has struggled with and recovered from my own eating disorder, I am familiar with this kind of reaction. When I found that I could no longer keep my suffering at bay, I rehearsed the words I wanted to say before mustering up the courage to tell my parents. Their response was dismissive at first, eventually evolving into frustration and then hopelessness. As much as they wanted me to get better, they didn’t understand why I was doing this to myself, and had no clue where to go for help. And when I tried to learn more about treatment and recovery on my own, I found that my background bore little resemblance to the movies I watched and the stories I read online. For a long time, it seemed like nobody understood quite how I felt.
While eating disorders certainly span all cultures, the way they are experienced can differ drastically depending on the culture in which an individual is raised. For me, being Asian felt like an obstacle to my recovery because I had trouble overcoming my shame and locating the resources I needed to get better. It is evident that the Asian American community is in desperate need of greater awareness and more resources catered to our experiences. Hiring people of different backgrounds and making efforts to provide intercultural awareness trainings for clinicians is a good place to start.
And to those who are recovered from or currently struggling with an eating disorder, don’t be afraid to talk about it. Allowing yourself to be vulnerable with someone you trust could be the first step to healing. It was for me. Uprooting a stigma that is so deeply entrenched in our culture can’t be done overnight, but we can start to chip away at it by exposing our suffering and finding strength in our shared experiences.
Like what you read? Check out Lauren’s final MEDA project, an E-Zine on the topic of eating disorders and body image in the Asian American community: https://issuu.com/kimlauren97/docs/eating_disorders_in_asian_america
[1] https://www.nationaleatingdisorders.org/people-color-and-eating-disorders
[2] http://www.mochimag.com/article/diagnosing-the-asian-american-eating-disorder/